In microeconomic theory, an indifference curve is a graph showing different bundles of goods between which a consumer is indifferent. That is, at each point on the curve, the consumer has no preference for one bundle over another. One can equivalently refer to each point on the indifference curve as rendering the same level of utility (satisfaction) for the consumer. Utility is then a device to represent preferences rather than something from which preferences come. The main use of indifference curves is in the representation of potentially observable demand patterns for individual consumers over commodity bundles.
There are infinitely many indifference curves: one passes through each combination. A collection of (selected) indifference curves, illustrated graphically, is referred to as an indifference map.
Properties of indifference curve:
There are infinitely many indifference curves: one passes through each combination. A collection of (selected) indifference curves, illustrated graphically, is referred to as an indifference map.
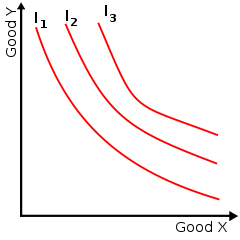 |
| An example of an indifference map with three indifference curves represented |
Properties of indifference curve:
- Slopes downward to the right
- Upward sloping
- Straight line parallel to X-axis
- Indifference curve cannot be parallel to the Y-axis
- Indifference curve is convex to the origin
- Downward sloping straight line
- Indifference curve cannot be concave to the origin
- Indifference curve cannot intersect each other
- Higher indifference curve represent higher level of satisfaction than lower IC
- Indifference curve need not be parallel

Comments
Post a Comment